|
Mutations in a subfamily of abscisic acid receptor genes promote rice growth and productivity
Thursday, 2018/06/07 | 08:06:36
|
|
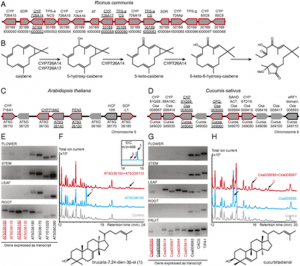
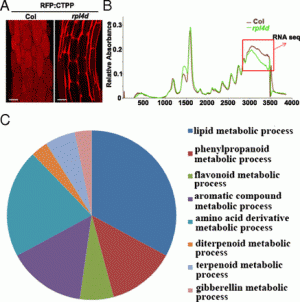
Chunbo Miao, Lihong Xiao, Kai Hua, Changsong Zou, Yang Zhao, Ray A. Bressan, and Jian-Kang Zhu PNAS June 5, 2018. 115 (23) 6058-6063 SignificanceClimate change is challenging plant agriculture and our ability to manage food security. Crop growth and yield are controlled by several phytohormones and their overlapping signal networks. We report here an unexpected aspect of the abscisic acid (ABA) signal network that directly impacts rice productivity. Simultaneously mutating the genes encoding the ABA receptors pyrabactin resistance 1-like 1 (PYL1), PYL4, and PYL6 causes improved growth and increased grain yield in rice. Our work thus reveals an important role of these ABA receptors in growth control and a genetic strategy to improve rice yield. AbstractAbscisic acid (ABA) is a key phytohormone that controls plant growth and stress responses. It is sensed by the pyrabactin resistance 1 (PYR1)/PYR1-like (PYL)/regulatory components of the ABA receptor (RCAR) family of proteins. Here, we utilized CRISPR/Cas9 technology to edit group I (PYL1–PYL6 and PYL12) and group II (PYL7–PYL11 and PYL13) PYL genes in rice. Characterization of the combinatorial mutants suggested that genes in group I have more important roles in stomatal movement, seed dormancy, and growth regulation than those in group II. Among all of the single pyl mutants, only pyl1 and pyl12 exhibited significant defects in seed dormancy. Interestingly, high-order group I mutants, but not any group II mutants, displayed enhanced growth. Among group I mutants, pyl1/4/6 exhibited the best growth and improved grain productivity in natural paddy field conditions, while maintaining nearly normal seed dormancy. Our results suggest that a subfamily of rice PYLs has evolved to have particularly important roles in regulating plant growth and reveal a genetic strategy to improve rice productivity.
See: http://www.pnas.org/content/115/23/6058
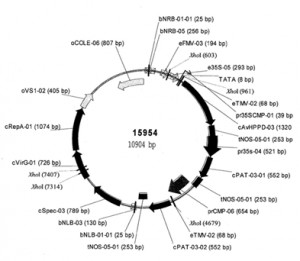
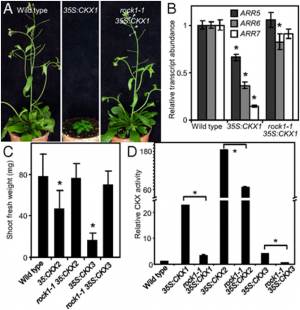
Figure 1: Group I pyl mutations promote rice growth. (A) Strategy of vector construction for editing rice PYL genes. (B) Comparison of wild-type, pyl1/6, pyl1/4/6, pyl1/2/3/4/6, pyl1/2/3/4/5/6, and pyl1/2/3/4/5/6/12 seedlings. (C) Shoot lengths and fresh weights of 21-d-old group I pyl seedlings. Every column represents an independent line. The “+” and “−” represent the wild-type and mutated genes, respectively. (D) Morphological features of wild-type, pyl1/2/3/4/5/6, and pyl1/4/6 plants at the mature stage. (E) Diameters of wild-type, pyl1/2/3/4/5/6, and pyl1/4/6 second internodes. (F) Comparison of the panicles and internodes of the wild type and pyl1/4/6. The arrowheads indicate the stem nodes. (Scale bars, 10 cm.) WT, wild type. Data are presented as means ± SD. P values (versus the wild type) were calculated by the Student’s t test: ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05. |
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
(35).png)