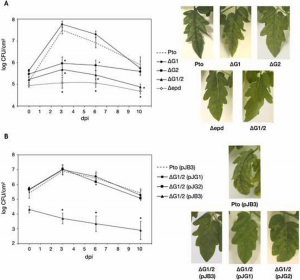
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH or Gap) is a ubiquitously distributed enzyme that plays an essential role in the glycolytic and gluconeogenic pathways. However, additional roles have been described unrelated to its enzymatic function in diverse organisms, often linked to its presence in the cell surface or as a secreted protein. Despite being a paradigm among multifunctional/moonlighting proteins, little is known about its possible roles in phytopathogenic bacteria.
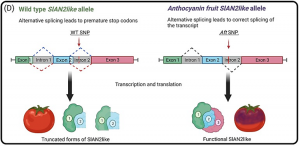
Over the past decade, progress has been made in the characterization of anthocyanin synthesis in fruits of plants belonging to the tomato clade. The genomic elements underlying the activation of the process were identified, providing the basis for understanding how the pathway works in these species. In this review we explore the genetic mechanisms that have been characterized to date, and detail the various wild relatives of the tomato
CRISPR/Cas is a breakthrough genome editing system because of its precision, target specificity and efficiency. As a speed breeding system, it is more robust than the conventional breeding and biotechnological approaches for qualitative and quantitative trait improvement. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) is an economically important crop but its yield and productivity have been severely impacted due to different abiotic and biotic stresses.
Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS), encoded by the mitochondrial open reading frames (ORFs), has long been used to economically produce crop hybrids. However, the utilization of CMS also hinders the exploitation of sterility and fertility variation in the absence of a restorer line, which in turn narrows the genetic background and reduces biodiversity. Here, we used a mitochondrial targeted transcription activator-like effector nuclease (mitoTALENs) to knock out ORF138 from the Ogura CMS broccoli hybrid.
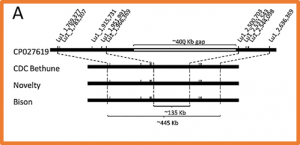
Fusarium wilt, caused by the soil-borne fungal pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lini, is a devastating disease in fax. Genetic resistance can counteract this disease and limit its spread. To map major genes for Fusarium wilt resistance, a recombinant inbred line population of more than 700 individuals derived from a cross between resistant cultivar ‘Bison’ and susceptible cultivar ‘Novelty’ was phenotyped in Fusarium wilt nurseries at two sites for two and three years, respectively.
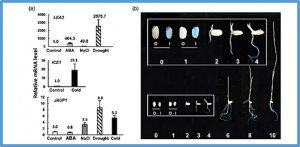
Root architecture and function are critical for plants to secure water and nutrient supply from the soil, but environmental stresses alter root development. The phytohormone jasmonic acid (JA) regulates plant growth and responses to wounding and other stresses, but its role in root development for adaptation to environmental challenges had not been well investigated. We discovered a novel JA Upregulated Protein 1 gene (JAUP1) that has recently evolved in rice and is specific to modern rice accessions
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) production is threatened by global warming associated with extreme high temperatures, and rice heat sensitivity is differed when stress occurs between daytime and nighttime. However, the underlying molecular mechanism are largely unknown. We show here that two glycine-rich RNA binding proteins, OsGRP3 and OsGRP162, are required for thermotolerance in rice, especially at nighttime. The rhythmic expression of OsGRP3/OsGRP162 peaks at midnight, and at these coincident times, is increased by heat stress. This is largely dependent on the evening complex component OsELF3-2.
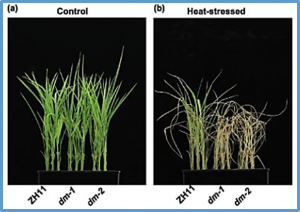
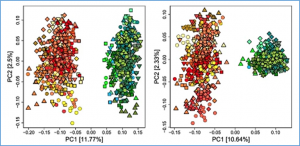
Solanum americanum serves as a promising source of resistance genes against potato late blight and is considered as a leafy vegetable for complementary food and nutrition. The limited availability of high-quality genome assemblies and gene annotations has hindered the exploration and exploitation of stress-resistance genes in S. americanum. Here, we present a chromosome-level genome assembly of a thermotolerant S. americanum ecotype and identify a crucial heat-inducible transcription factor gene, SaHSF17, essential for heat tolerance.
Starting a hybrid breeding program commonly comprises a grouping of the initial germplasm in two pools and subsequent selection on general combining ability. Investigations on pre-breeding steps before starting the selection on general combining ability are not available. Our goals were (1) to use computer simulations on the basis of DNA markers and testcross data to plan crosses that separate genetically two initial germplasm pools of rapeseed,
High temperature is the most important environmental factor limiting potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) yield. The tuber yield has been used to evaluate the heat tolerance of some potato cultivars, but potato yield was closely correlated with the maturation period. Therefore, it is necessary to employ different parameters to comprehensively analyze and evaluate potato tolerance to heat stress.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :