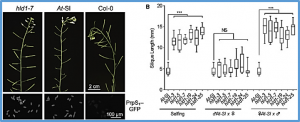
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins (GPI-APs) are tethered to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane where they function as key regulators of a plethora of biological processes in eukaryotes. Self-incompatibility (SI) plays a pivotal role regulating fertilization in higher plants through recognition and rejection of “self” pollen. Here, we used Arabidopsis thaliana lines that were engineered to be self-incompatible by expression of Papaver rhoeas SI determinants for an SI suppressor screen. We identify HLD1/AtPGAP1, an ortholog of the human GPI-inositol deacylase PGAP1, as a critical component required for the SI response.
Plants and animals are in constant association with a variety of microbes. Although much is known about how pathogenic and symbiotic microbes interact with plants, less is known about the population dynamics, adaptive traits, and transcriptional features of the vast number of microbes that make up the bulk of the plant microbiota. The majority of microbiota taxa are either commensal, natural mutants of pathogens, or pathogens that encounter strong immune responses due to plant recognition of pathogen effectors
Invasive social insects are among the most damaging of invasive organisms and have proved universally intractable to biological control. Despite this, populations of some invasive social insects collapse from unknown causes. We report long-term studies demonstrating that infection by a microsporidian pathogen causes populations of a globally significant invasive ant to collapse to local extinction, providing a mechanistic understanding of a pervasive phenomenon in biological invasions: the collapse of established populations from endogenous factors. We apply this knowledge and successfully eliminate two large, introduced populations of these ants.
Genetic diversity is a prerequisite for crop improvement. This study, which was carried out at Patuakhali Science and Technology University, Bangladesh, explored the genetic diversity of 38 Bangladeshi aus rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces under drought stress by using phenotypic and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Nonhierarchal clustering analysis with Mahalanobis‟ D2 statistic based on the data of morphological traits divided the studied landraces into four groups
Phosphorus (P) is essential for cellular processes like respiration, photosynthesis, biosynthesis of membrane phospholipids, etc. To cope with P deficiency stress, plants adopt reprograming of the expression of genes involved in different metabolic/signaling pathways for survival, growth, and development. Plants use transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and/or post-translational machinery to achieve P homeostasis.
Seed coat color is related to flavonoid content which is closely related to seed dormancy. According to the genetic analysis of a six-generation population derived from two parents (IC2508 with a yellow seed coat and IC2518 with a brown seed coat), we discovered that the yellow seed coat trait in melon is controlled by a single dominant gene, named CmBS-1. Bulked segregant analysis sequencing (BSA-Seq) revealed that the gene is located at 11,860,000–15,890,000 bp (4.03 Mb) on Chr 6
White lupin (Lupinus albus L.) is a promising grain legume to meet the growing demand for plant-based protein. Its cultivation, however, is severely threatened by anthracnose disease caused by the fungal pathogen Colletotrichum lupini. To dissect the genetic architecture for anthracnose resistance, genotyping by sequencing was performed on white lupin accessions collected from the center of domestication and traditional cultivation regions.
Wheat yields are stagnating around the world and new sources of genes for resistance or tolerances to abiotic traits are required. In this context, the tetraploid wheat wild relatives are among the key candidates for wheat improvement. Despite its potential huge value for wheat breeding, the tetraploid GGAtAt genepool is largely neglected. Understanding the population structure, native distribution range, intraspecific variation of the entire tetraploid GGAtAt genepool and its domestication history would further its use for wheat improvement.
Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a global commodity, and its production is a key component underpinning worldwide food security. Yellow rust, also known as stripe rust, is a wheat disease caused by the fungus Puccinia striiformis Westend f. sp. tritici (Pst), and results in yield losses in most wheat growing areas. Recently, the rapid global spread of genetically diverse sexually derived Pst races, which have now largely replaced the previous clonally propagated slowly evolving endemic populations, has resulted in further challenges for the protection of global wheat yields.
Cyanogenic glucosides (CGs) play a key role in host-plant defense to insect feeding; however, the metabolic tradeoffs between synthesis of CGs and plant growth are not well understood. In this study, genetic mutants coupled with nondestructive phenotyping techniques were used to study the impact of the CG dhurrin on fall armyworm [Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith)] (FAW) feeding and plant growth in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. A genetic mutation in CYP79A1 gene that disrupts dhurrin biosynthesis was used to develop sets of near-isogenic lines (NILs) with contrasting dhurrin contents in the Tx623 bmr6 genetic background.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :