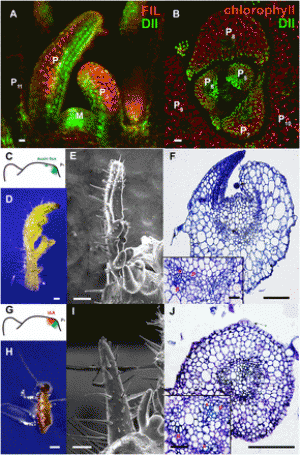
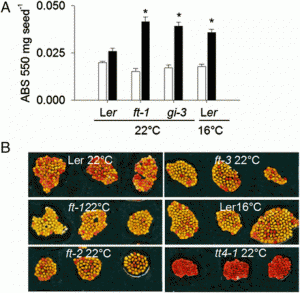
|
Characterization of ZmPMP3g function in drought tolerance of maize
Thursday, 2023/07/27 | 08:00:05
|
|
Ling Lei, Hong Pan, Hai-Yang Hu, Xian-Wei Fan, Zhen-Bo Wu, You-Zhi Li Sci Rep.; 2023 May 5; 13(1):7375. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32989-4. AbstractThe genes enconding proteins containing plasma membrane proteolipid 3 (PMP3) domain are responsive to abiotic stresses, but their functions in maize drought tolerance remain largely unknown. In this study, the transgenic maize lines overexpressing maize ZmPMP3g gene were featured by enhanced drought tolerance; increases in total root length, activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase, and leaf water content; and decreases in leaf water potential, levels of O2-·and H2O2, and malondialdehyde content under drought. Under treatments with foliar spraying with abscisic acid (ABA), drought tolerance of both transgenic line Y7-1 overexpressing ZmPMP3g and wild type Ye478 was enhanced, of which Y7-1 showed an increased endogenous ABA and decreased endogenous gibberellin (GA) 1 (significantly) and GA3 (very slightly but not significantly) and Ye478 had a relatively lower ABA and no changes in GA1 and GA3. ZmPMP3g overexpression in Y7-1 affected the expression of multiple key transcription factor genes in ABA-dependent and -independent drought signaling pathways. These results indicate that ZmPMP3g overexpression plays a role in maize drought tolerance by harmonizing ABA-GA1-GA3 homeostasis/balance, improving root growth, enhancing antioxidant capacity, maintaining membrane lipid integrity, and regulating intracellular osmotic pressure. A working model on ABA-GA-ZmPMP3g was proposed and discussed.
See https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37147346/
A working model related to ZmPMP3g overexpression. This model was established based on gene expression data in this study, of which the effects and paths of gene and enzyme actions referred to the literature36–38,46,47,49,50,61–65. Enhanced expression of ZmPMP3g gene would result in three major effects toward the following routes: (1) repressing the expression of some ABI5s, DELLAs, and WRKYs (WRKY2, WRKY6, WRKY32 and WRKY55), and therefore relieving from maize growth restriction caused by elevated ABA; (2) inducing expression of ABI5 and NCED8, promoting ABA production, and consequently endowing maize with drought tolerance; and (3) facilitating expression of GID12 and GA20ox5, and GA1 production, and therefore improving maize growth under drought. In these processes, the cross-talk between the expression of related genes and production of ABA and GA occurred. The red and green boxes indicated an up-regulation/increase and a down-regulation/decrease in gene expression/ABA or GA production, respectively. The dashed lines with arrows denoted that the routes and/or their actions are unknown. The italics indicated genes. ABA, Abscisic acid; ABI5, ABA-insensitive 5; GA, Gibberellin; GA2ox, GA2-oxidase; GA20ox, GA20-oxidase; GID1L2, GA receptor; NCED, Nine-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase. WRKY, WRKY transcription factor.
|
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
(259).png)