|
Owen Hudson, Marcio F. R. Resende Jr., Charlie Messina, James Holland & Jeremy Brawner
Theoretical and Applied Genetics; August 2024; vol.137; article 196
(240).png)
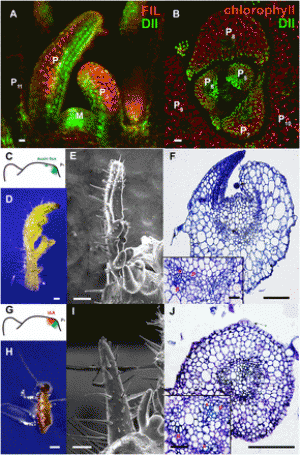
Figure: Maize Fusarium kernel rot
Key message
Integrating disease screening data and genomic data for host and pathogen populations into prediction models provides breeders and pathologists with a unified framework to develop disease resistance.
Abstract
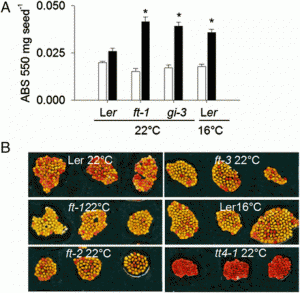
Developing disease resistance in crops typically consists of exposing breeding populations to a virulent strain of the pathogen that is causing disease. While including a diverse set of pathogens in the experiments would be desirable for developing broad and durable disease resistance, it is logistically complex and uncommon, and limits our capacity to implement dual (host-by-pathogen)-genome prediction models. Data from an alternative disease screening system that challenges a diverse sweet corn population with a diverse set of pathogen isolates are provided to demonstrate the changes in genetic parameter estimates that result from using genomic data to provide connectivity across sparsely tested experimental treatments. An inflation in genetic variance estimates was observed when among isolate relatedness estimates were included in prediction models, which was moderated when host-by-pathogen interaction effects were incorporated into models. The complete model that included genomic similarity matrices for host, pathogen, and interaction effects indicated that the proportion of phenotypic variation in lesion size that is attributable to host, pathogen, and interaction effects was similar. Estimates of the stability of lesion size predictions for host varieties inoculated with different isolates and the stability of isolates used to inoculate different hosts were also similar. In this pathosystem, genetic parameter estimates indicate that host, pathogen, and host-by-pathogen interaction predictions may be used to identify crop varieties that are resistant to specific virulence mechanisms and to guide the deployment of these sources of resistance into pathogen populations where they will be more effective.
See https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00122-024-04698-7
(234).png)
Figure 2: Histograms summarizing phenotypic data as treatment means. A displays the mean disease severity for each Fusarium isolate scored using kernel counting. B describes the same phenotypic data; however, values are presented for each maize variety
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
(240).png)
(234).png)