|
Review: miRNAs and lncRNAs in tomato: Roles in biotic and abiotic stress responses
Tuesday, 2023/03/07 | 08:08:08
|
|
Qian Li, Heng Shen, Shoujuan Yuan, Xigang Dai, Changxian Yang Front Plant Science; 2023 Jan 11; 13:1094459. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1094459. AbstractPlants are continuously exposed to various biotic and abiotic stresses in the natural environment. To cope with these stresses, they have evolved a multitude of defenses mechanisms. With the rapid development of genome sequencing technologies, a large number of non-coding RNA (ncRNAs) have been identified in tomato, like microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). Recently, more and more evidence indicates that many ncRNAs are involved in plant response to biotic and abiotic stresses in tomato. In this review, we summarize recent updates on the regulatory roles of ncRNAs in tomato abiotic/biotic responses, including abiotic (high temperature, drought, cold, salinization, etc.) and biotic (bacteria, fungi, viruses, insects, etc.) stresses. Understanding the molecular mechanisms mediated by ncRNAs in response to these stresses will help us to clarify the future directions for ncRNA research and resistance breeding in tomato.
See https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36714724/
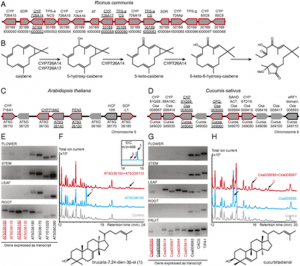
miRNAs regulate tomato response to abiotic stresses. miR319d was induced by low temperature to inhibit the expression of target genes GAMYB-like1 and improving tomato cold tolerance (Shi et al., 2019). miR166 was also induced to express by low temperature. When embryonic development is blocked, low temperature induces parthenocarpy in heterozygous genotype plants (Clepet et al., 2021). Low temperature will down-regulate the expression of miR164a/b-5p, release the inhibition of NAM3, and improve the cold tolerance of tomato (Dong et al., 2022). High temperature upregulates the expression of miR319d and miR169, and inhibiting the transcription of downstream target genes to improve tomato heat tolerance (Shi et al., 2019; Rao et al., 2022). However, the target genes of miR319d at high temperature are unknown. miR169c and miR156 were up-regulated under drought, inhibited the expression of downstream transcription factors, and improved tomato tolerance to drought (Zhang et al., 2011; Visentin et al., 2020). While miR1916 and miR396 were down-regulated under drought condition, regulating downstream signaling pathways to improve tomato tolerance to drought (Chen et al., 2019; Fracasso et al., 2021). The target genes of miR1916 under drought stress are currently unknown. Low potassium stress induces the expression of miR168, inhibits the expression of AGO1, and enhances K+ uptake by regulating downstream signaling pathways (Liu et al., 2020).
|
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
(103).png)